Large Language Models
Introduction to LLMs
History of LLMs
A Survey of Large Language Models
大型語言模型(>10B)的時間軸

計算記憶體的成長與Transformer大小的關係
Scaling Law
我們可以用模型大小、Dataset大小、總計算量,來預測模型最終能力。(通常以相對簡單的函數型態, ex: Linear relationship)
GPT-4 Technical Report. OpenAI. 2023
Blog: 【LLM 10大觀念-1】Scaling Law
Papers:
- Hestness et al. 於2017發現在Machine Translation, Language Modeling, Speech Recognition和Image Classification都有出現Scaling law.
- OpenAI Kaplan et al.2020 於2020年從計算量、Dataset大小、跟參數量分別討論了Scaling Law。
- Rosenfeld et al. 於2021年發表了關於Scaling Law的survey paper。在各種architecture更進一步驗證Scaling Law的普適性。
Chinchilla Scaling Law
Paper: Training Compute-Optimal Large Language Models
如果我們接受原本Scaling Law的定義(模型性能可藉由參數量、Dataset大小、計算量預測),馬上就會衍伸出兩個很重要的問題:
Return(收益): 在固定的訓練計算量之下,我們所能得到的最好性能是多好?
Allocation(分配):我們要怎麼分配我們的模型參數量跟Dataset大小。
(假設計算量 = 參數量 * Dataset size,我們要大模型 * 少量data、中模型 * 中量data、還是小模型 * 大量data)
2022年DeepMind提出Chinchilla Scaling Law,同時解決了這兩個問題,並且依此改善了當時其他大模型的訓練方式。
他們基於三種方式來找到訓練LLM的Scaling Law:
- 固定模型大小,變化訓練Data數量。
- 固定計算量(浮點運算),變化模型大小。
- 對所有實驗結果,直接擬合參數化損失函數。

Method 3 result from Chinchilla Scaling Law,N是模型參數量、D是數據量、其他都是係數
LLM最終的Loss(Perplexity),會隨著模型放大、數據量變多而下降,並且是跟他們呈現指數映射後線性關係。
Chinchilla最大的貢獻更是在解決Allocation的問題,他們發現
- 數據量(Tokens數)應該要約等於模型參數量的20倍
- 並且數據量跟模型參數量要同比放大(Ex: 模型放大一倍,數據也要跟著增加一倍)
Large Language Models
Open LLM Leaderboard
Transformer
Paper: Attention Is All You Need

ChatGPT
ChatGPT: Optimizing Language Models for Dialogue
ChatGPT is fine-tuned from a model in the GPT-3.5 series, which finished training in early 2022.
GPT4
Paper: GPT-4 Technical Report
 Paper: From Sparse to Dense: GPT-4 Summarization with Chain of Density Prompting
Paper: From Sparse to Dense: GPT-4 Summarization with Chain of Density Prompting
Blog: GPT-4 Code Interpreter: The Next Big Thing in AI
LLaMA
Paper: LLaMA: Open and Efficient Foundation Language Models
 Blog: Building a Million-Parameter LLM from Scratch Using Python
Blog: Building a Million-Parameter LLM from Scratch Using Python
Kaggle: LLM LLaMA from scratch
BloombergGPT
Paper: BloombergGPT: A Large Language Model for Finance
Blog: Introducing BloombergGPT, Bloomberg’s 50-billion parameter large language model, purpose-built from scratch for finance
Pythia
Paper: Pythia: A Suite for Analyzing Large Language Models Across Training and Scaling
Dataset:
The Pile: An 800GB Dataset of Diverse Text for Language Modeling
Datasheet for the Pile
Code: Pythia: Interpreting Transformers Across Time and Scale
MPT-7B
model: mosaicml/mpt-7b-chat
Code: https://github.com/mosaicml/llm-foundry
Blog: Announcing MPT-7B-8K: 8K Context Length for Document Understanding
Blog: Introducing MPT-7B: A New Standard for Open-Source, Commercially Usable LLMs
Falcon-40B
model: tiiuae/falcon-40b
Paper: The RefinedWeb Dataset for Falcon LLM: Outperforming Curated Corpora with Web Data, and Web Data Only
Orca
Paper: Orca: Progressive Learning from Complex Explanation Traces of GPT-4
OpenLLaMA
model: openlm-research/open_llama_3b_v2
model: openlm-research/open_llama_7b_v2
Code: https://github.com/openlm-research/open_llama
Kaggle: https://www.kaggle.com/code/rkuo2000/llm-openllama
Vicuna
model: lmsys/vicuna-7b-v1.5
Paper: Judging LLM-as-a-Judge with MT-Bench and Chatbot Arena
Code: https://github.com/lm-sys/FastChat
LLaMA-2
model: meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hf
Paper: Llama 2: Open Foundation and Fine-Tuned Chat Models
Code: https://github.com/facebookresearch/llama
Sheared LLaMA
model_name = “princeton-nlp/Sheared-LLaMA-1.3B”, princeton-nlp/Sheared-LLaMA-2.7B | princeton-nlp/Sheared-Pythia-160m
Paper: Sheared LLaMA: Accelerating Language Model Pre-training via Structured Pruning
Code: https://github.com/princeton-nlp/LLM-Shearing
Neural-Chat-7B (Intel)
model_name = “Intel/neural-chat-7b-v3-1”
Blog: Intel neural-chat-7b Model Achieves Top Ranking on LLM Leaderboard!
Mistral
model_name = “mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2”
Paper: Mistral 7B
Code: https://github.com/mistralai/mistral-src
Kaggle: https://www.kaggle.com/code/rkuo2000/llm-mistral-7b-instruct

Mistral 8X7B
model: mistralai/Mixtral-8x7B-v0.1
Paper: Mixtral of Experts

Starling-LM
model: Nexusflow/Starling-LM-7B-beta
Paper: RLAIF: Scaling Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback with AI Feedback
Blog: Starling-7B: Increasing LLM Helpfulness & Harmlessness with RLAIF

Zephyr
model: HuggingFaceH4/zephyr-7b-beta
Paper: Zephyr: Direct Distillation of LM Alignment
Kaggle: https://www.kaggle.com/code/rkuo2000/llm-zephyr-7b
 Blog: Zephyr-7B : HuggingFace’s Hyper-Optimized LLM Built on Top of Mistral 7B
Blog: Zephyr-7B : HuggingFace’s Hyper-Optimized LLM Built on Top of Mistral 7B

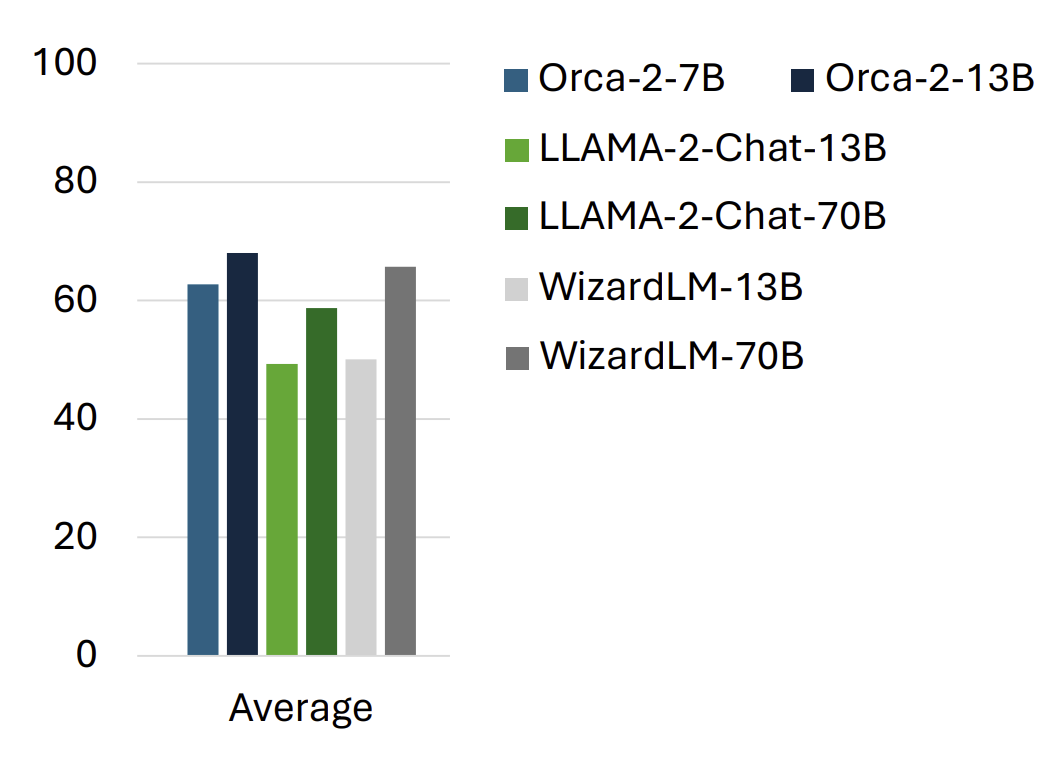
Orca 2
model: microsoft/Orca-2-7b
Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2311.11045
Blog: Microsoft’s Orca 2 LLM Outperforms Models That Are 10x Larger
BlueLM (VIVO)
model: vivo-ai/BlueLM-7B-Chat-4bits
Code: https://github.com/vivo-ai-lab/BlueLM/
Taiwan-LLM (優必達+台大)
model: yentinglin/Taiwan-LLM-7B-v2.1-chat
Paper: TAIWAN-LLM: Bridging the Linguistic Divide with a Culturally Aligned Language Model
Blog: 專屬台灣!優必達攜手台大打造「Taiwan LLM」,為何我們需要本土化的AI?
Code: https://github.com/MiuLab/Taiwan-LLM
Phi-2 (Transformer with 2.7B parameters)
model: microsoft/phi-2
Blog: Phi-2: The surprising power of small language models
Kaggle: https://www.kaggle.com/code/rkuo2000/llm-phi-2
Mamba
model: Q-bert/Mamba-130M
Paper: Mamba: Linear-Time Sequence Modeling with Selective State Spaces
Kaggle: https://www.kaggle.com/code/rkuo2000/llm-mamba-130m
Kaggle: https://www.kaggle.com/code/rkuo2000/llm-mamba-3b

SOLAR-10.7B ~ Depth Upscaling
Paper: SOLAR 10.7B: Scaling Large Language Models with Simple yet Effective Depth Up-Scaling
Code: https://huggingface.co/upstage/SOLAR-10.7B-v1.0
Depth-Upscaled SOLAR-10.7B has remarkable performance. It outperforms models with up to 30B parameters, even surpassing the recent Mixtral 8X7B model.
Leveraging state-of-the-art instruction fine-tuning methods, including supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and direct preference optimization (DPO),
researchers utilized a diverse set of datasets for training. This fine-tuned model, SOLAR-10.7B-Instruct-v1.0, achieves a remarkable Model H6 score of 74.20,
boasting its effectiveness in single-turn dialogue scenarios.
Qwen (通义千问)
model: Qwen/Qwen1.5-7B-Chat
Blog: Introducing Qwen1.5
Code: https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen1.5
Yi (零一万物)
model: 01-ai/Yi-6B-Chat
Paper: CMMMU: A Chinese Massive Multi-discipline Multimodal Understanding Benchmark
Paper: Yi: Open Foundation Models by 01.AI
Orca-Math
Paper: Orca-Math: Unlocking the potential of SLMs in Grade School Math
Dataset: https://huggingface.co/datasets/microsoft/orca-math-word-problems-200k
BitNet
Paper: BitNet: Scaling 1-bit Transformers for Large Language Models
Paper: The Era of 1-bit LLMs: All Large Language Models are in 1.58 Bits
bitnet.cpp is the official inference framework for 1-bit LLMs (e.g., BitNet b1.58).

Gemma
model: google/gemma-1.1-7b-it
Blog: Gemma: Introducing new state-of-the-art open models
Kaggle: https://www.kaggle.com/code/nilaychauhan/fine-tune-gemma-models-in-keras-using-lora
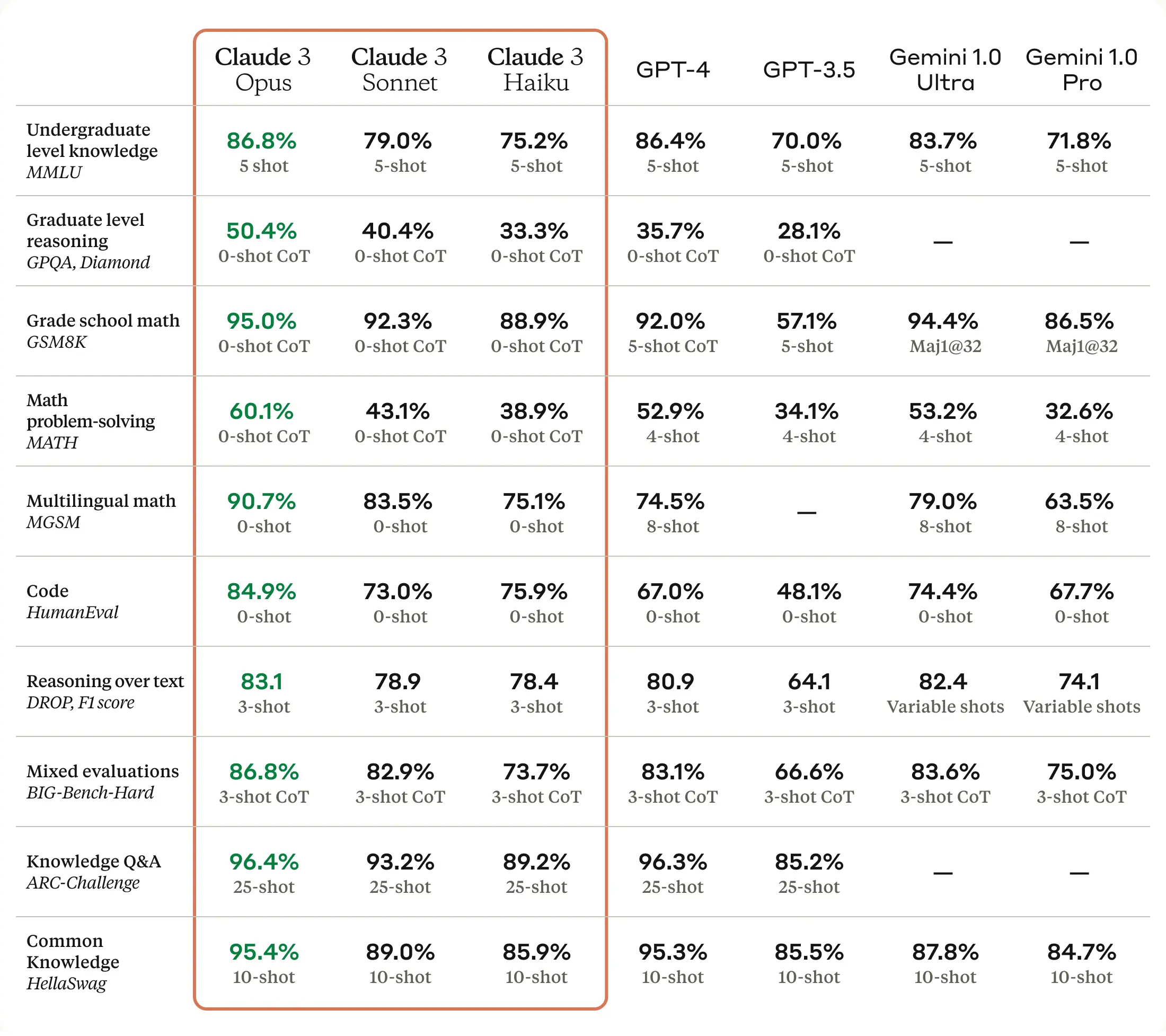
Gemini-1.5
Claude 3
Breeze (達哥)
model: MediaTek-Research/Breeze-7B-Instruct-v0_1
Paper: Breeze-7B Technical Report
Blog: Breeze-7B: 透過 Mistral-7B Fine-Tune 出來的繁中開源模型
Bialong (白龍)
Paper: Bailong: Bilingual Transfer Learning based on QLoRA and Zip-tie Embedding
model: INX-TEXT/Bailong-instruct-7B
TAIDE
model: taide/TAIDE-LX-7B-Chat
- TAIDE-LX-7B: 以 LLaMA2-7b 為基礎,僅使用繁體中文資料預訓練 (continuous pretraining)的模型,適合使用者會對模型進一步微調(fine tune)的使用情境。因預訓練模型沒有經過微調和偏好對齊,可能會產生惡意或不安全的輸出,使用時請小心。
- TAIDE-LX-7B-Chat: 以 TAIDE-LX-7B 為基礎,透過指令微調(instruction tuning)強化辦公室常用任務和多輪問答對話能力,適合聊天對話或任務協助的使用情境。TAIDE-LX-7B-Chat另外有提供4 bit 量化模型,量化模型主要是提供使用者的便利性,可能會影響效能與更多不可預期的問題,還請使用者理解與注意。
InflectionAI
Blog: Inflection AI 發表新基礎模型「Inflection-2.5 」,能力逼近 GPT-4!
Phind-70B
Blog: Introducing Phind-70B – closing the code quality gap with GPT-4 Turbo while running 4x faster
Blog: Phind - 給工程師的智慧搜尋引擎
Llama-3
model: meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct
Code: https://github.com/meta-llama/llama3/

Phi-3
model: microsoft/Phi-3-mini-4k-instruct”
Blog: Introducing Phi-3: Redefining what’s possible with SLMs
Octopus v4
model: NexaAIDev/Octopus-v4
Paper: Octopus v4: Graph of language models
Code: https://github.com/NexaAI/octopus-v4
design demo
Llama 3.1
mode: meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct

Grok-2
Grok-2 & Grok-2 mini, achieve performance levels competitive to other frontier models in areas such as graduate-level science knowledge (GPQA), general knowledge (MMLU, MMLU-Pro), and math competition problems (MATH). Additionally, Grok-2 excels in vision-based tasks, delivering state-of-the-art performance in visual math reasoning (MathVista) and in document-based question answering (DocVQA).

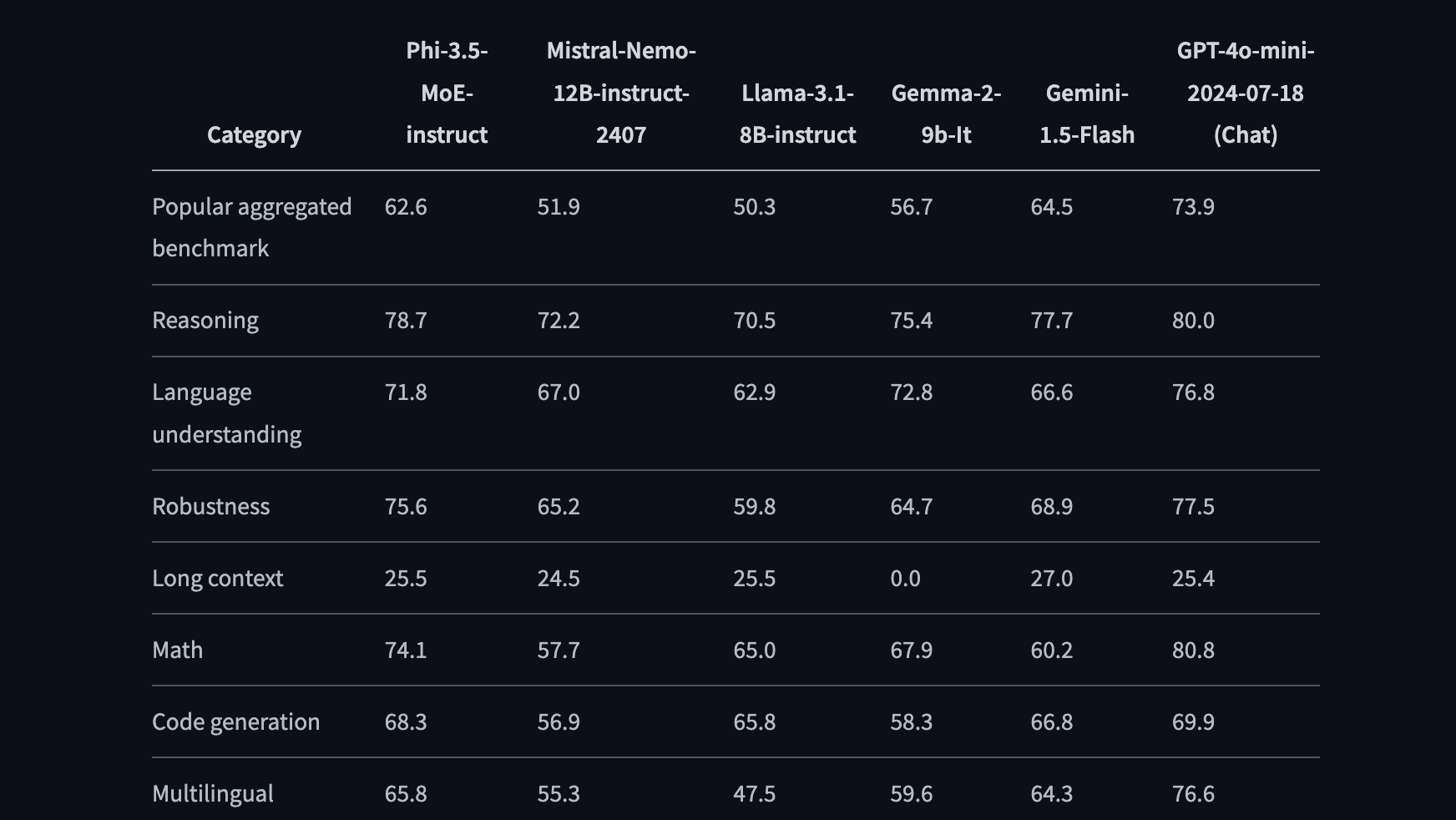
Phi-3.5
model: microsoft/Phi-3.5-mini-instruct
model: microsoft/Phi-3.5-vision-instruct
model: microsoft/Phi-3.5-MoE-instruct
News: Microsoft Unveils Phi-3.5: Powerful AI Models Punch Above Their Weight
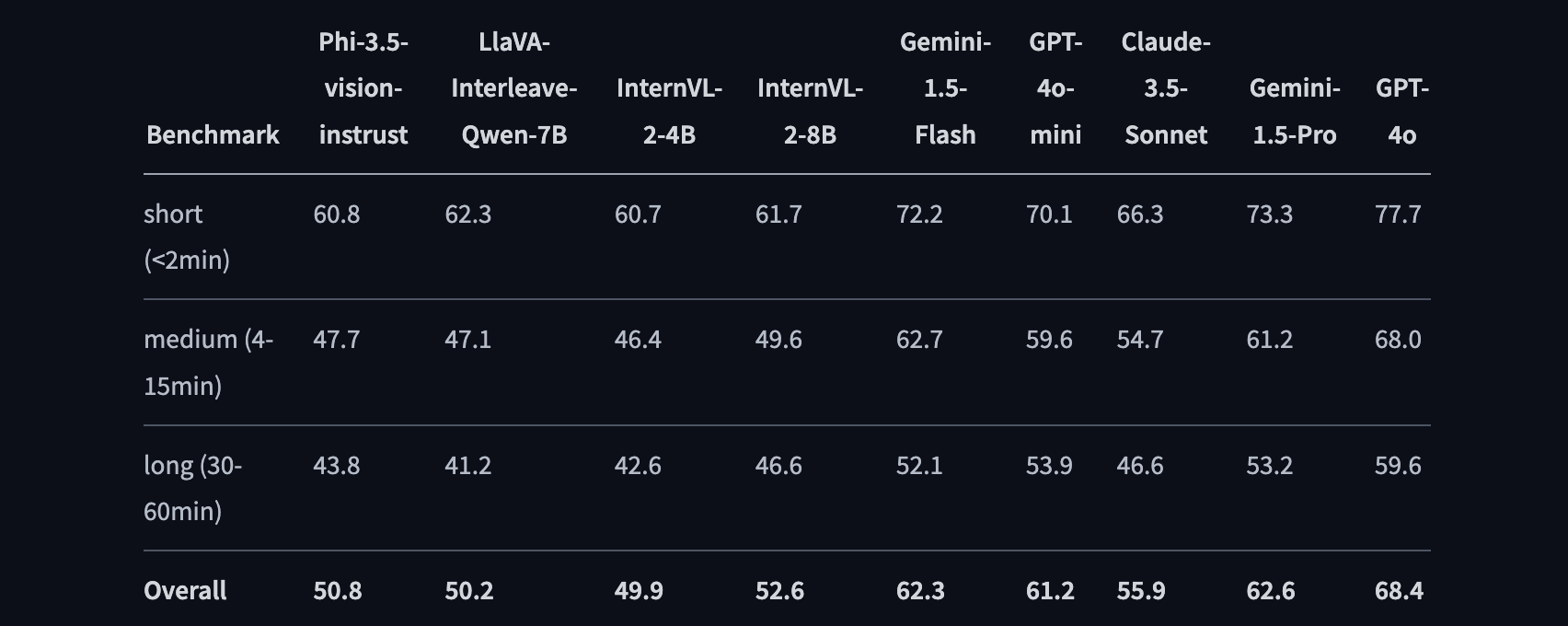
OpenAI o1
Blog: Introducing OpenAI o1-preview

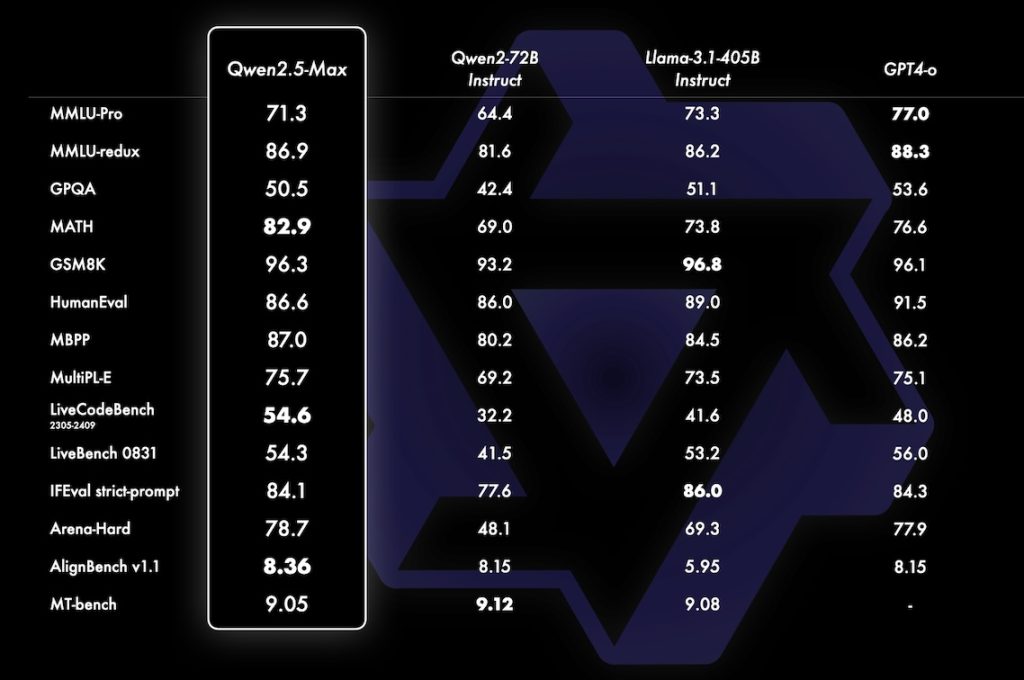
Qwen2.5
model: Qwen/Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct
- Qwen2.5: 0.5B, 1.5B, 3B, 7B, 14B, 32B, 72B
- Qwen2.5-Coder: 1.5B, 7B, coming 32B
- Qwen2.5-Math: 1.5B, 7B, 72B
Blog: 阿里雲AI算力大升級!發佈100個開源Qwen 2.5模型及視頻AI模型
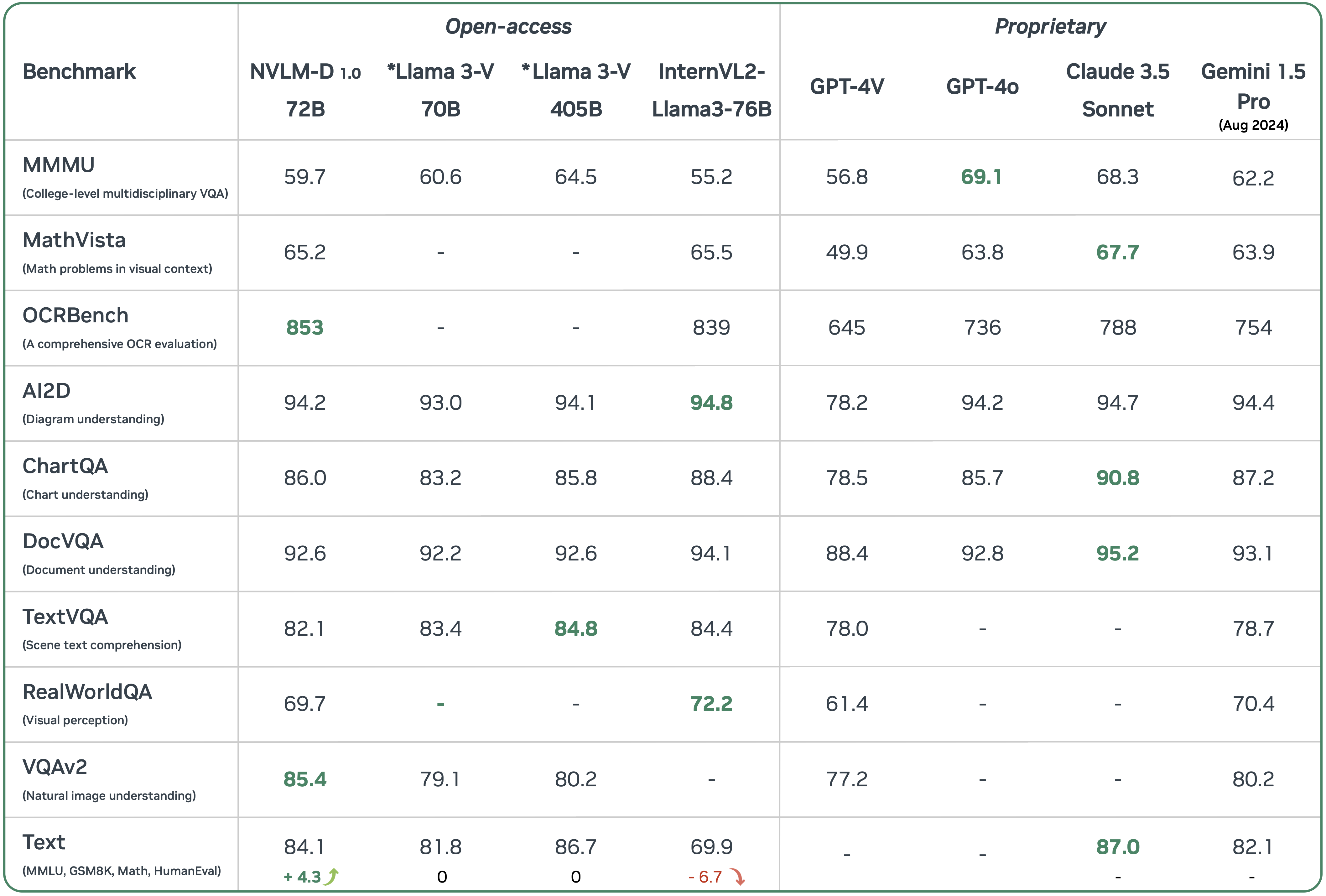
NVLM 1.0
Paper: NVLM: Open Frontier-Class Multimodal LLMs
Llama 3.2
Blog: Llama 3.2: Revolutionizing edge AI and vision with open, customizable models
model: meta-llama/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct
model: meta-llama/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct
model: meta-llama/Llama-3.2-11B-Vision-Instruct

LFM Liquid-3B
Aria
model: rhymes-ai/Aria
Llama 3.3
model: meta-llama/Llama-3.3-70B-Instruct
Blog: Meta公布輕巧版多語言模型Llama 3.3
OpenAI o3-mini

DeepSeek-R1
Paper: DeepSeek-R1: Incentivizing Reasoning Capability in LLMs via Reinforcement Learning
Code: https://github.com/deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1

Goedel-Prover
Code: https://github.com/Goedel-LM/Goedel-Prover

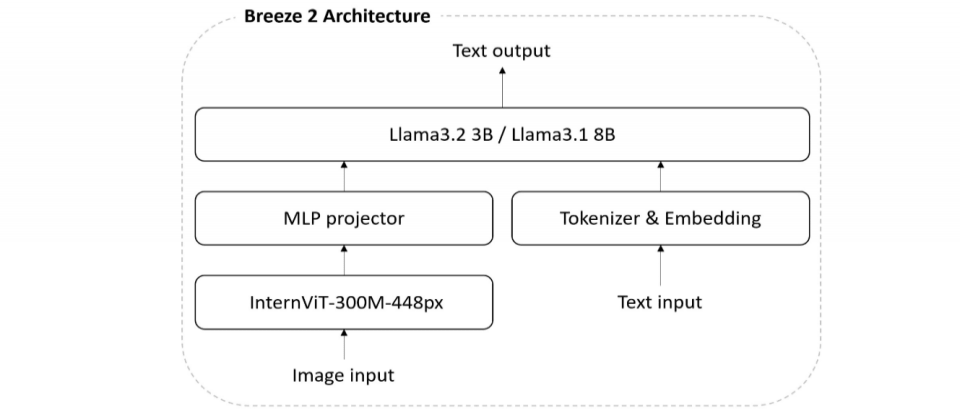
Llama-Breeze2
model: MediaTek-Research/Llama-Breeze2-8B-Instruct
model: MediaTek-Research/Llama-Breeze2-3B-Instruct
Paper: The Breeze 2 Herd of Models: Traditional Chinese LLMs Based on Llama with Vision-Aware and Function-Calling Capabilities
Blog:** 聯發科一口氣開源2款繁中多模態小模型、符合臺灣口音的語音合成模型
Blog:** 如何讓模型更懂繁中知識?聯發科研究團隊揭技術關鍵
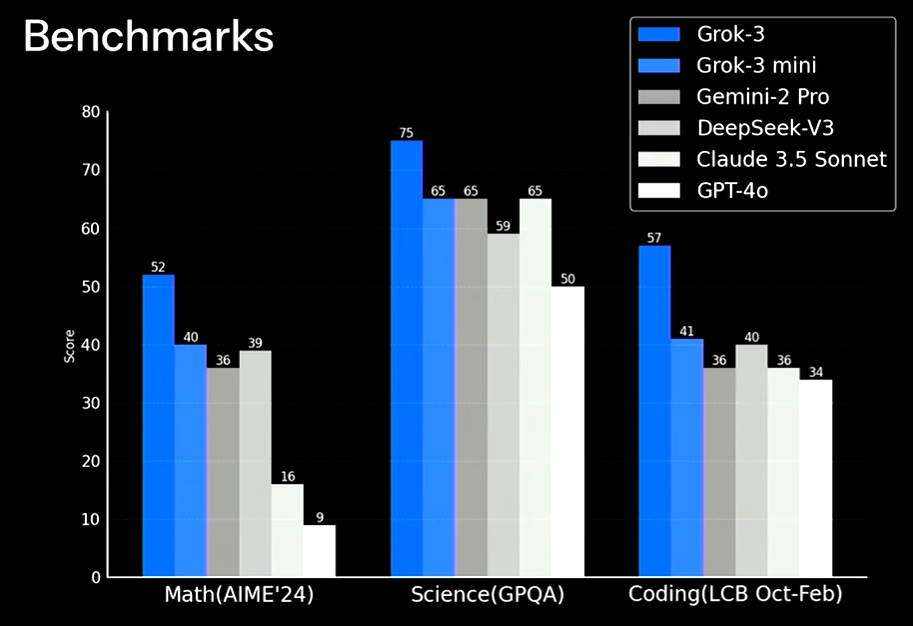
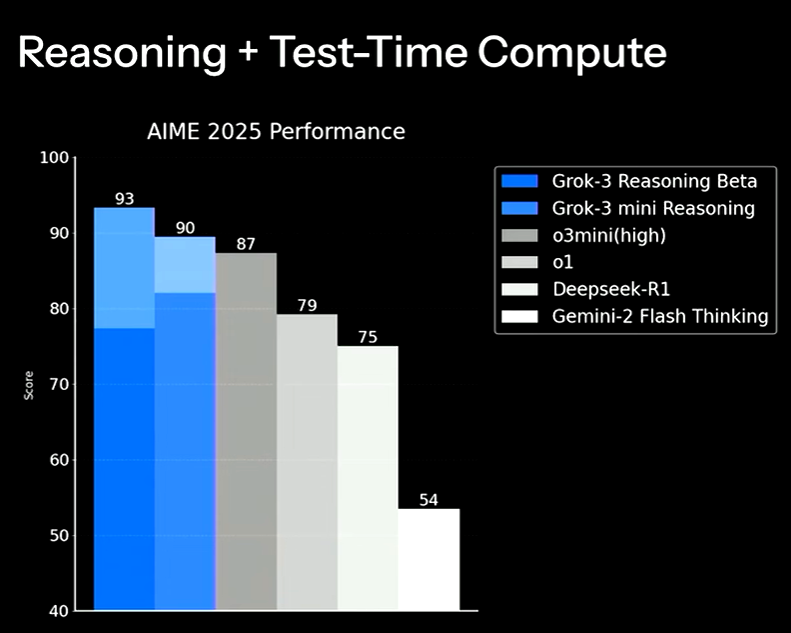
Grok-3
Phi-4-multimodal
Phi-4-multimodal具有56億參數,支援12.8萬Token的上下文長度,並透過監督式微調、直接偏好最佳化(DPO)與人類回饋強化學習(RLHF)等方式,提升指令遵循能力與安全性。在語言支援方面,文字處理涵蓋超過20種語言,包括中文、日文、韓文、德文與法文等,語音處理則涵蓋英語、中文、西班牙語、日語等主要語種,圖像處理目前則以英文為主。
model microsoft/Phi-4-multimodal-instruct

safe AI
Constitutional AI
Paper: Constitutional AI: Harmlessness from AI Feedback
Two key phases:
- Supervised Learning Phase (SL Phase)
- Step1: The learning starts using the samples from the initial model
- Step2: From these samples, the model generates self-critiques and revisions
- Step3: Fine-tine the original model with these revisions
- Reinforcement Learning Phase (RL Phease)
- Step1. The model uses samples from the fine-tuned model.
- Step2. Use a model to compare the outputs from samples from the initial model and the fine-tuned model
- Step3. Decide which sample is better. (RLHF)
- Step4. Train a new “preference model” from the new dataset of AI preferences. This new “prefernece model” will then be used to re-train the RL (as a reward signal). It is now the RLHAF (Reinforcement Learning from AI feedback)
Attack LLM
Blog 如何攻擊 LLM (ChatGPT) ?
- JailBreak
- Prompt Injection
- Data poisoning
LLM running locally
LM Studio

ollama
ollama -v
ollama
ollama pull deepseek-r1
ollama run llama3.2
Code: Github
Kaggle: Langchain RAG
Jan
Github: https://github.com/janhq/jan
PrivateGPT
Code: https://github.com/zylon-ai/private-gpt/tree/primordial

GPT4All
chmod +x gpt4all-installer-linux.run
./gpt4all-installer-linux.run
cd ~/gpt4all
./bin/chat
GPT4FREE
pip install g4f
llama.cpp
Reasoning
我在杯子裡放一個草莓, 把杯子倒過來放在桌上, 再把杯子放到微波爐裡, 請問草莓在哪?
- Gemini

- ChatGPT

- Llama3.2


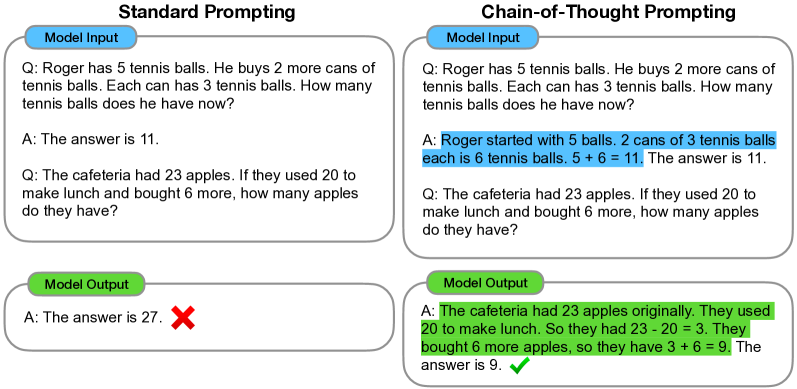
Chain-of-Thought Prompting
Paper: Chain-of-Thought Prompting Elicits Reasoning in Large Language Models
ReAct Prompting
Paper: ReAct: Synergizing Reasoning and Acting in Language Models
Code: https://github.com/ysymyth/ReAct

Tree-of-Thoughts
Paper: Tree of Thoughts: Deliberate Problem Solving with Large Language Models
Code: https://github.com/princeton-nlp/tree-of-thought-llm
Code: https://github.com/kyegomez/tree-of-thoughts

Tabular CoT
Paper: Tab-CoT: Zero-shot Tabular Chain of Thought
Code: https://github.com/Xalp/Tab-CoT

Chain of thought and ReAct — SQL Agent

Survey of Chain-of-Thought
Paper: A Survey of Chain of Thought Reasoning: Advances, Frontiers and Future
訓練不了人工智慧?你可以訓練你自己
Thinking Claude
17歲高中生寫出「神級Prompt」強化Claude推理能力媲美o1模型,如何實現?
Thinking Gemini
https://github.com/lanesky/thinking-gemini
Reasoning Language Models
Paper: Reasoning Language Models: A Blueprint
This site was last updated September 16, 2025.

